[Algorithm] BFS & DFS (feat.Java)
zl존석동
·2022. 2. 15. 21:04
그래프 자료 탐색 방법인 깊이우선탐색(DFS)과 너비우선탐색(BFS)에 대해 공부하고 기록해보자
그래프
정점(Node)과 정점을 연결하는 간선(Edge)으로 구성된 자료구조를 말한다.
특정한 하나의 정점에서는 간선으로 연결된 다른 정점들을 방문할 수 있다.

BFS와 DFS는 하나의 정점에서 시작해 그래프의 모든 정점들을 탐색하려할 때의 방법들로
어떤 순서대로 모든 정점들을 방문할지에 차이가 있다.
그래프를 인접 리스트 와 인접 행렬 방법으로 표현할 수 있다.
인접 행렬 방법
int[][] adjArray = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjArray[v1][v2] = 1;
adjArray[v2][v1] = 1;
}
adjArray[v1][v2] = 1;
adjArray[v2][v1] = 1;
기본적으로 정점간의 간선이 양방향이라고 생각한다면 반드시 두 방향에 모두 연결이 있음을 표현해주어야 한다.
주어지는 그래프의 크기가 너무 크거나 간선이 별로 없는 희소그래프에서는 인접 행렬 방법은 비효율적이니 사용하지 말자
인접 리스트 방법
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjList[v1].add(v2);
adjList[v2].add(v1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Collections.sort(adjList[i]);
}
LinkedList 컬렉션을 활용하며 역시 양방향일 때 양쪽에 모두 값이 있어야 한다.
깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS: Depth First Search)
깊이 우선이라는 말 그대로 하나의 정점에서 시작해 갈 수 있는 곳 까지 깊게 가는 방법이다.
더 이상 갈 곳이 없을 때까지 탐색한 뒤 이전 탐색 정점으로 돌아와 또 다른 간선을 찾아 탐색하는 것이다.
DFS 알고리즘
0. 방문여부를 체크할 배열이 있다.
1. 탐색 시작 정점을 스택에 넣는다.
2. 스택이 비어있지 않다면 3번 4번을 할거다.
3. 스택에서 정점 하나를 꺼낸다.
4. 방문하지 않았다면 방문표시를 하고 인접한 모든 정점들중 방문하지 않은 것들을 스택에 넣는다.
다음과 같은 그래프에서 숫자 0 인 정점부터 시작해 모든 정점을 탐색한다고 생각해보자.
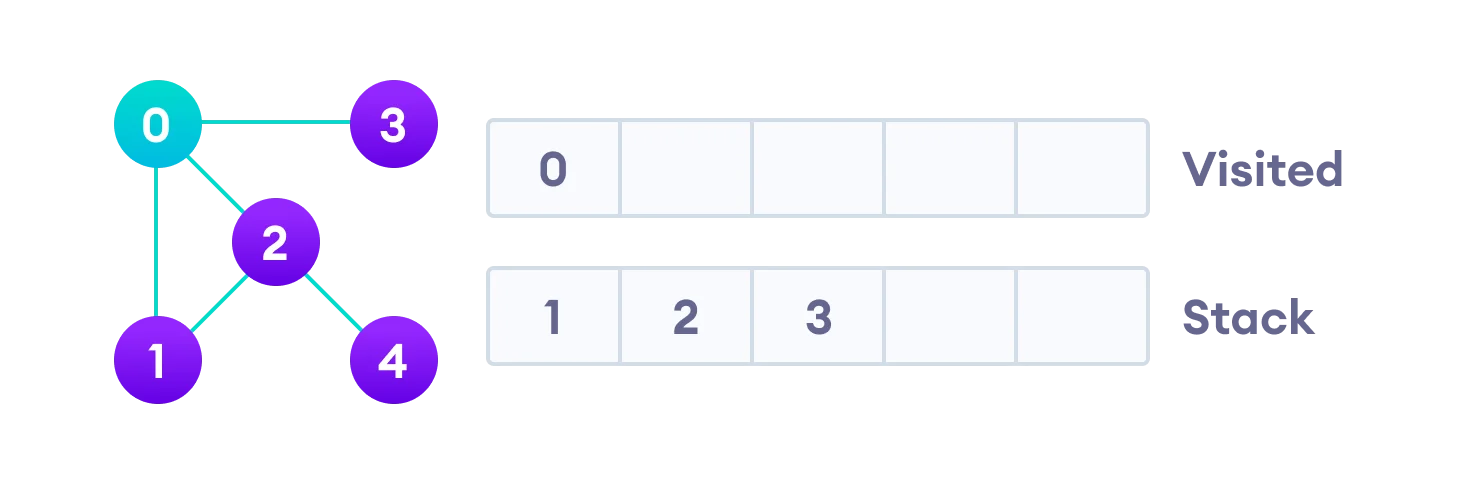
- 0을 먼저 방문하기에 Visited 에 0 을 체크한다.
- 0 과 바로 인접하여 연결된 정점들을 Stack 에 넣는다. 0과 인접한 3,2,1 이 들어가게 된다.

- 1,2,3 이외에 더 이상 0과 연결된 노드는 없었다.
- 따라서 Stack의 맨위의 값에 있는 (0과 연결되었던 정점인) 1을 탐색한다.
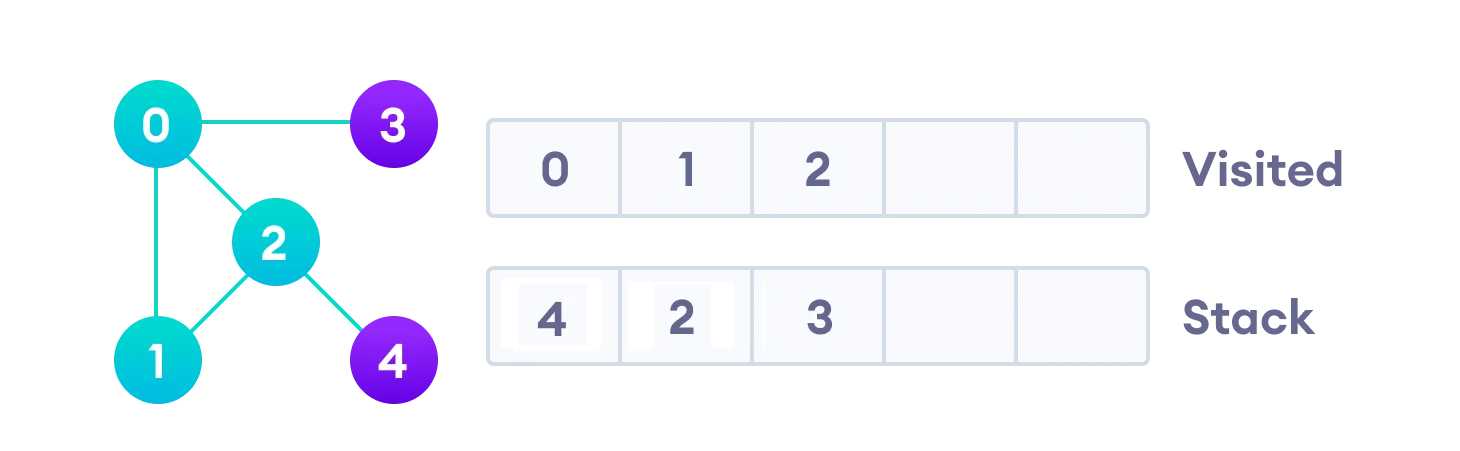
- 1과 연결된 노드들을 살펴보면 0과 2가 있다.
- 0의 경우는 Visited 라 Stack에 넣지 않는다.
- 2의 경우는 방문하지 않았기에 Stack에 넣어준다.
- 더 이상 1과 연결된 노드가 없기에 2를 방문해주고 방문하지 않은 2의 인접 정점인 4를 Stack에 넣어준다.
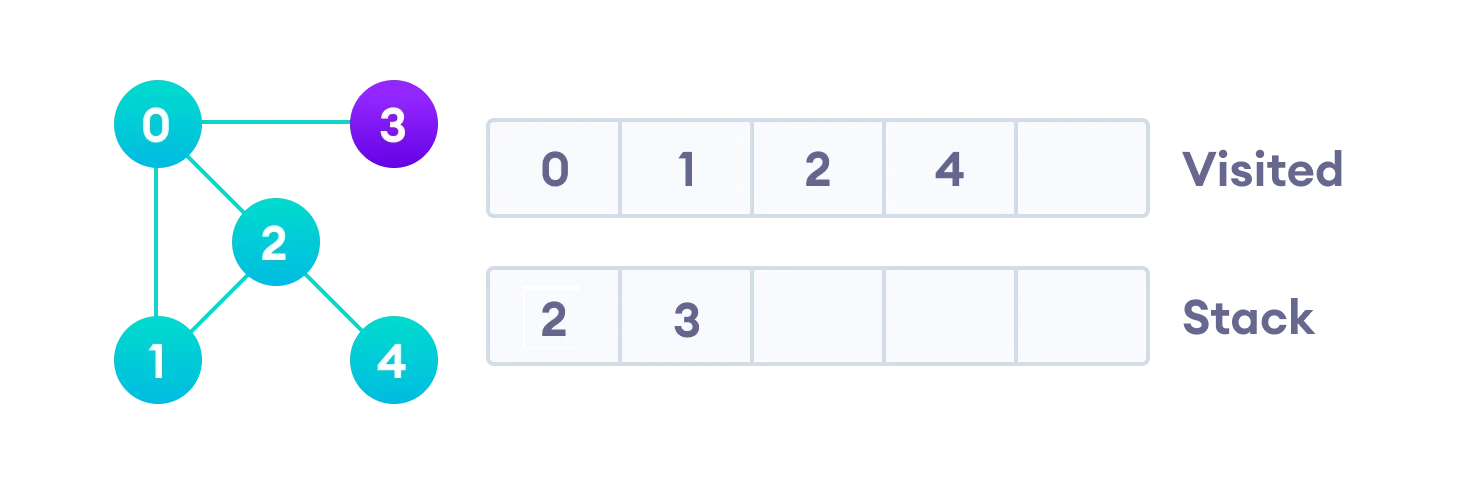
- 2와 연결된 노드가 더 이상 없으니 Stack 맨 위의 4를 방문한다.
- 그러고 Stack 맨 위를 보니 2가 남는다. 하지만 2는 Visited이기 때문에 그대로 Pop 해준다.

- 마지막 남은 3을 방문하고 나면 Stack이 비게 되고 그래프 탐색이 완료된다.!
DFS가 좋을 때
- 모든 노드들을 완전 탐색하고자 할 때
- 경로마다 특징이 있을 때 [예: 같은 경로에는 같은 숫자가 없어야 한다.]
- 자료구조가 매우 넓을 때
- BackTracking
DFS Java Code
스택과 재귀로 모두 구현할 수 있다.
DFS - 인접리스트
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int node = sc.nextInt();
int edge = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
boolean visited[] = new boolean[node + 1];
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[node + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= node; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjList[v1].add(v2);
adjList[v2].add(v1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= node; i++) {
Collections.sort(adjList[i]);
}
DFS(start, adjList, visited);
}
public static void DFS(int start, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, boolean[] visited) {
visited[start] = true;
System.out.print(start + " ");
Iterator<Integer> iter = adjList[start].listIterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
int adj = iter.next();
if (!visited[adj])
DFS(adj, adjList, visited);
}
}
}
DFS - 인접 행렬
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int node = sc.nextInt();
int edge = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
boolean visited[] = new boolean[node + 1];
int[][] adjArray = new int[node + 1][node + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjArray[v1][v2] = 1;
adjArray[v2][v1] = 1;
}
DFS(start, adjArray, visited);
}
public static void DFS(int start, int[][] adjArray, boolean[] visited) {
visited[start] = true;
System.out.print(start + " ");
for (int i = 1; i < adjArray.length; i++) {
if (adjArray[start][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
DFS(i, adjArray, visited);
}
}
}
}
너비 우선 탐색 (BFS: Breadth First Search)
특정한 정점에서 시작할 때 해당 정점과 가까운 정점들을 먼저 방문하고 멀리 있는 정점을 나중에 방문하는 방법이다.
좀 어처구니 없는 예시같긴 하지만
옥동자나 누가바 같은 아이스크림을 먹을 때 꼭 순서대로 안 먹고 껍데기부터 벗겨가며 먹었던 변태같은 사람들을 생각해보면 된다.
넓게 퍼져있는 부분부터 공략해가며 안으로 깊게 들어가는 방식이다.
BFS 알고리즘
0. 방문여부를 체크할 배열이 있다.
1. 시작 정점을 큐에 넣으며 탐색을 시작한다.
2. 큐가 비어있지 않을 동안 3번과 4번을 수행할 것이다.
3. 큐에서 정점 하나를 꺼낸다.
4. 방문하지 않았다면 방문표시를 하고 방문하지 않았던 인접 노드들을 모두 큐에 넣는다.
다음과 같은 그래프에서 숫자 0 인 정점부터 시작해 모든 정점을 탐색한다고 생각해보자.

- 맨 처음 Queue에 넣었던 시작 정점인 0 을 Queue에서 꺼내며 Visited 에 포함시킨다.
- 정점 0 과 인접한 1 , 2 , 3 정점들을 모두 큐에 넣는다.

- Queue의 맨 앞에 있는 1을 빼와 Visited 에 포함시킨다.
- 정점 1과 인접한 정점들 중 방문하지 않았던 정점 2를 큐에 넣는다.
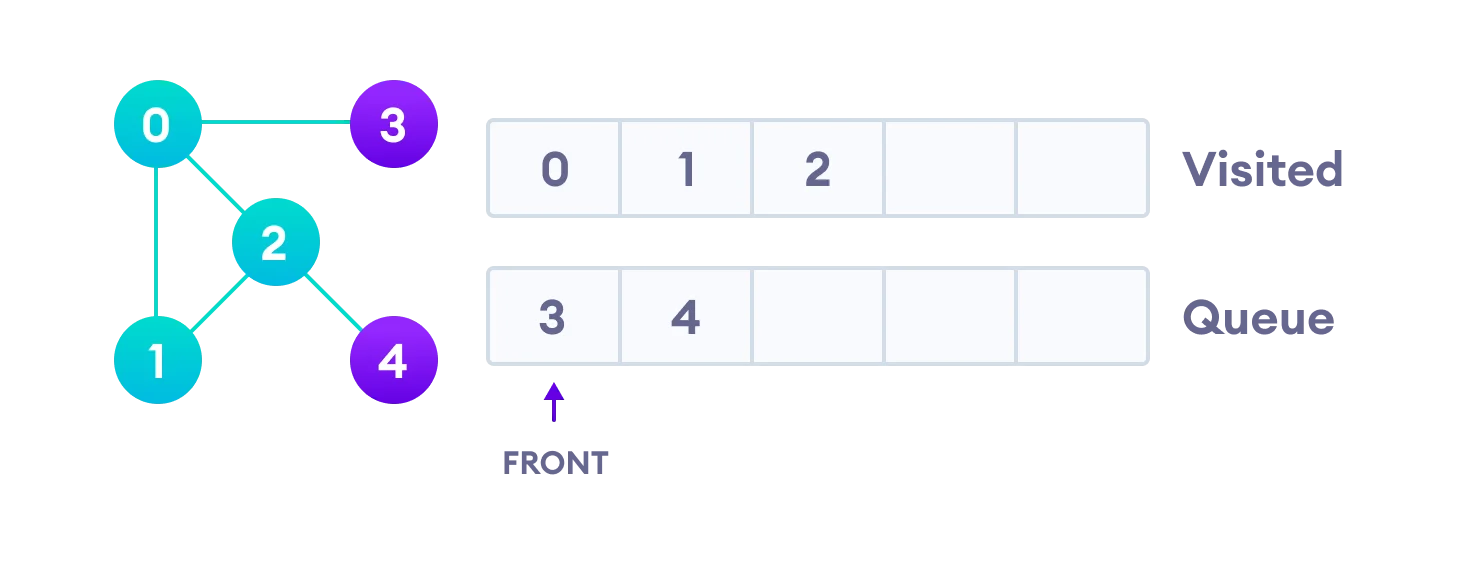
- 마찬가지로 2를 Queue에서 빼며 Visited 처리한다.
- 그러면서 2와 인접해있는 정점 4를 큐에 넣는다.
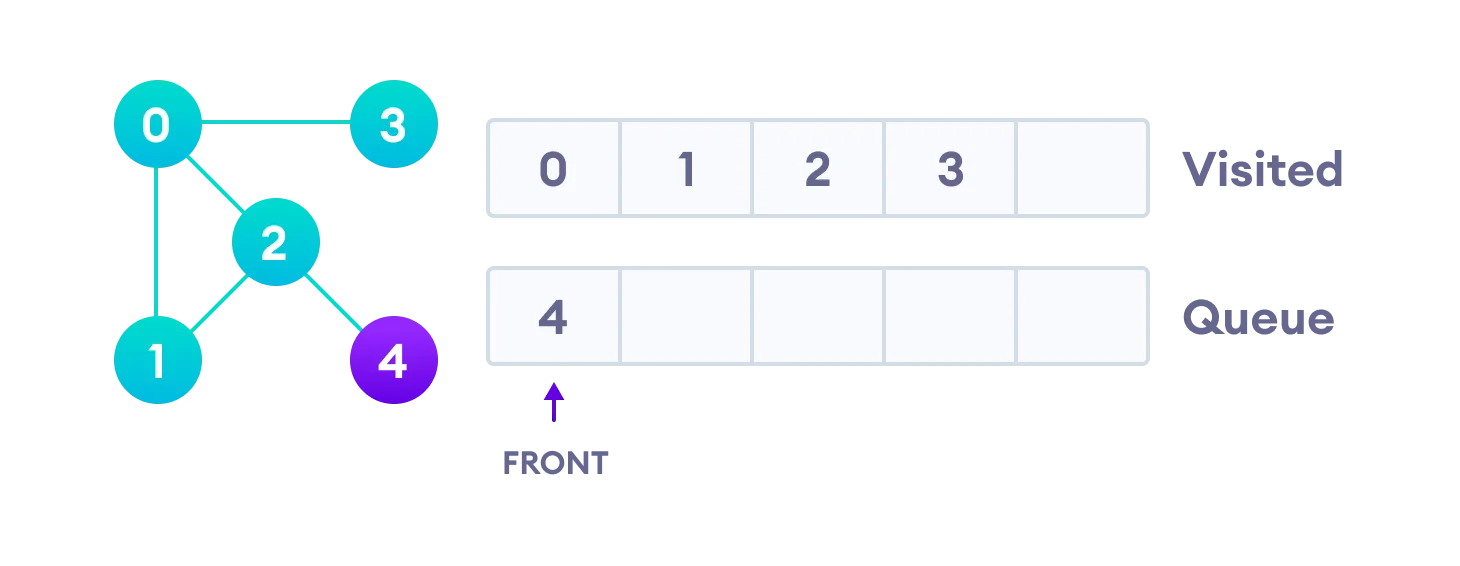
- 마찬가지로 3을 Queue에서 뺀다. 이제 넣어야할 인접 정점은 없다.
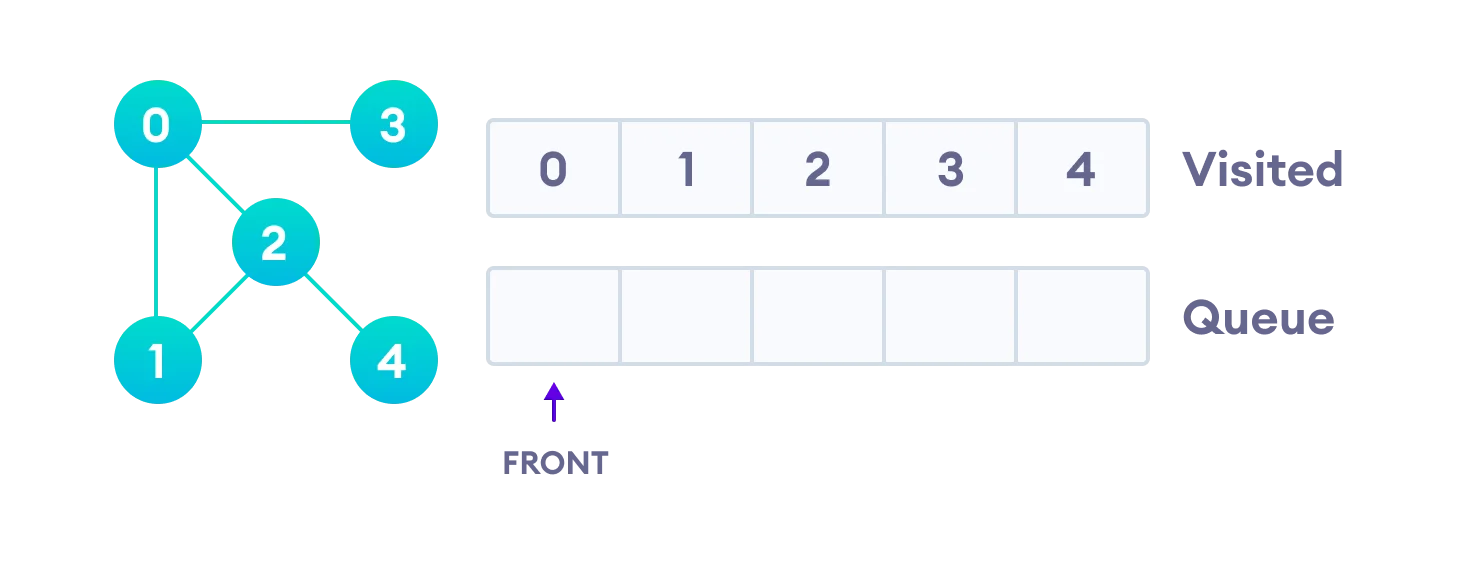
- Queue에 있던 정점 4를 빼고 Visited 처리를 하여 그래프 탐색이 종료된다.!
BFS가 좋을 때
- 두 정점 사이의 최단거리를 찾아야 할 때
- 솔루션이 탐색 시작지점(루트) 과 멀지 않다는 것을 알 때
- 트리가 아주 깊고 솔루션이 드문 경우
BFS Java Code
Queue 로 구현한다.
BFS - 인접 리스트
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int node = sc.nextInt();
int edge = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
boolean visited[] = new boolean[node + 1];
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[node + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= node; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjList[v1].add(v2);
adjList[v2].add(v1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= node; i++) {
Collections.sort(adjList[i]);
}
BFS(start, adjList, visited);
}
public static void BFS(int start, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
visited[start] = true;
queue.add(start);
while(queue.size() != 0) {
start = queue.poll();
System.out.print(start + " ");
Iterator<Integer> iter = adjList[start].listIterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
int adj = iter.next();
if(!visited[adj]) {
visited[adj] = true;
queue.add(adj);
}
}
}
}
}
BFS - 인접 행렬 구현
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int node = sc.nextInt();
int edge = sc.nextInt();
int start = sc.nextInt();
boolean visited[] = new boolean[node + 1];
int[][] adjArray = new int[node + 1][node + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < edge; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjArray[v1][v2] = 1;
adjArray[v2][v1] = 1;
}
BFS(start, adjArray, visited);
}
public static void BFS(int start, int[][] adjArray, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
start = queue.poll();
System.out.print(start + " ");
for (int i = 1; i < adjArray.length; i++) {
if (adjArray[start][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
queue.add(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
연습하기 좋은 문제
BFS DFS 두 가지 그래프 탐색 방법의 원형을 코드로 구현해볼 수 있는 좋은 문제인 것 같다.
이론적으로는 어떻게 돌아가는지 알겠는데 코드로 직접 구현하려고 하면 꽤 어려운 것 같다.
1260번: DFS와 BFS
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), 간선의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호 V가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 간선이 연결하는 두 정점의 번호가 주어진다. 어떤 두 정점 사
www.acmicpc.net
Ref
Depth First Search (DFS) Algorithm
Depth First Search (DFS) In this tutorial, you will learn about depth first search algorithm with examples and pseudocode. Also, you will learn to implement DFS in C, Java, Python, and C++. Depth first Search or Depth first traversal is a recursive algorit
www.programiz.com
BFS Graph Algorithm(With code in C, C++, Java and Python)
Breadth first search In this tutorial, you will learn about breadth first search algorithm. Also, you will find working examples of bfs algorithm in C, C++, Java and Python. Traversal means visiting all the nodes of a graph. Breadth First Traversal or Brea
www.programiz.com
[알고리즘] 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS) 과 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
[알고리즘] 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)과 너비 우선 탐색(BFS) 그래프를 탐색하는 방법에는 크게 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)과 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)이 있습니다. 📌여기서 그래프란, 정점(node)과 그 정점을 연
devuna.tistory.com
'알고리즘 & 자료구조 > Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] 이분 탐색 (0) | 2022.01.21 |
|---|


